注記
最後まで移動して、完全なサンプルコードをダウンロードするか、Binder経由でブラウザでこの例を実行してください
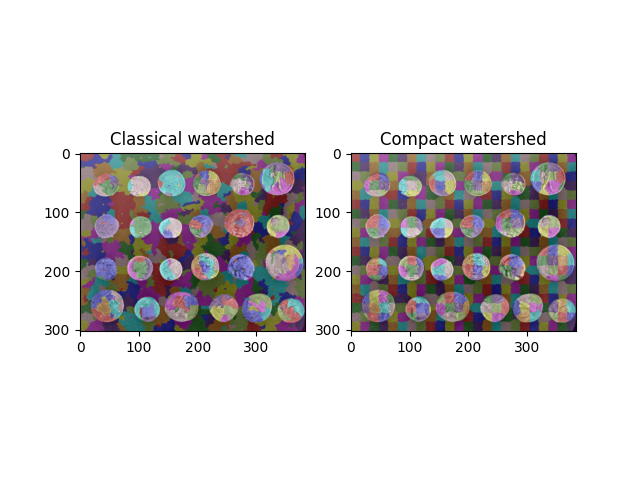
コンパクトなウォーターシェッドを使用して規則的なセグメントを見つける#
ウォーターシェッド変換は、多くのセグメンテーションアルゴリズムの出発点として一般的に使用されます。ただし、適切なシードを選択しないと、非常に不均一なフラグメントサイズが生成される可能性があり、ダウンストリーム分析で処理するのが難しい場合があります。
コンパクトなウォーターシェッド変換は、考慮されているピクセルに近いシードを優先することにより、これを改善します。
両方のアルゴリズムは、skimage.segmentation.watershed() 関数で実装されています。コンパクトな形式を使用するには、compactness 値を0より大きくするだけで済みます。
import numpy as np
from skimage import data, util, filters, color
from skimage.segmentation import watershed
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
coins = data.coins()
edges = filters.sobel(coins)
grid = util.regular_grid(coins.shape, n_points=468)
seeds = np.zeros(coins.shape, dtype=int)
seeds[grid] = np.arange(seeds[grid].size).reshape(seeds[grid].shape) + 1
w0 = watershed(edges, seeds)
w1 = watershed(edges, seeds, compactness=0.01)
fig, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax0.imshow(color.label2rgb(w0, coins, bg_label=-1))
ax0.set_title('Classical watershed')
ax1.imshow(color.label2rgb(w1, coins, bg_label=-1))
ax1.set_title('Compact watershed')
plt.show()
スクリプトの総実行時間: (0分0.451秒)
