注記
最後まで移動して、完全な例コードをダウンロードします。または、Binder経由でブラウザでこの例を実行します。
Marching Cubes#
Marching cubesは、3Dボリュームから2Dサーフェスメッシュを抽出するアルゴリズムです。これは、地形図や天気図の等高線に対する3Dの一般化と考えることができます。関心のあるレベルを横切る領域を探してボリューム全体を反復処理することで機能します。そのような領域が見つかると、三角形分割が生成され、出力メッシュに追加されます。最終的な結果は、頂点のセットと三角形面のセットです。
このアルゴリズムには、データボリュームとアイソサーフェス値が必要です。たとえば、CT画像では、+700〜+3000のハウンズフィールドユニットが骨を表します。したがって、潜在的な入力の1つは、再構成されたCTデータセットと値+700であり、骨または骨のような密度の領域のメッシュを抽出します。
この実装は、spacingキーワード引数を使用することで、すべての空間次元でボクセル間隔が等しくない異方性データセットでも正しく機能します。
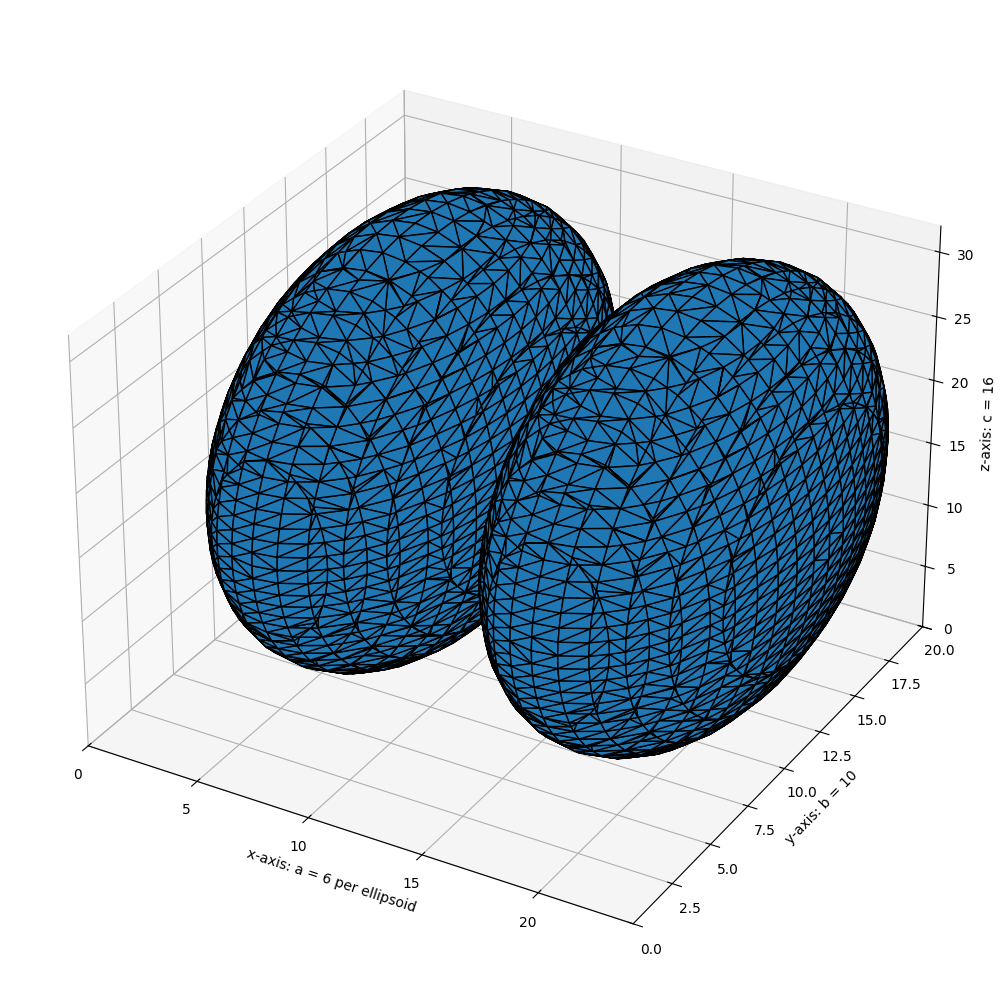
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection
from skimage import measure
from skimage.draw import ellipsoid
# Generate a level set about zero of two identical ellipsoids in 3D
ellip_base = ellipsoid(6, 10, 16, levelset=True)
ellip_double = np.concatenate((ellip_base[:-1, ...], ellip_base[2:, ...]), axis=0)
# Use marching cubes to obtain the surface mesh of these ellipsoids
verts, faces, normals, values = measure.marching_cubes(ellip_double, 0)
# Display resulting triangular mesh using Matplotlib. This can also be done
# with mayavi (see skimage.measure.marching_cubes docstring).
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# Fancy indexing: `verts[faces]` to generate a collection of triangles
mesh = Poly3DCollection(verts[faces])
mesh.set_edgecolor('k')
ax.add_collection3d(mesh)
ax.set_xlabel("x-axis: a = 6 per ellipsoid")
ax.set_ylabel("y-axis: b = 10")
ax.set_zlabel("z-axis: c = 16")
ax.set_xlim(0, 24) # a = 6 (times two for 2nd ellipsoid)
ax.set_ylim(0, 20) # b = 10
ax.set_zlim(0, 32) # c = 16
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
**スクリプトの総実行時間:**(0分1.807秒)
